If you’ve ever stood in front of a massive stockpile in a mine, a steel plant, or a cement yard, you know how overwhelming it looks. Mountains of coal, limestone, iron ore, or bauxite stacked high, constantly being added to or taken away. For the people managing these stockyards, the big question is simple yet critical: How much material do we actually have?
For decades, industries have struggled with this. Counting truckloads, using measuring tapes, or relying on ground survey teams—all of these methods take time, involve risks, and often lead to inaccurate numbers. And when millions of rupees or dollars depend on knowing your stock precisely, “rough estimates” just don’t cut it.
This is where drones have quietly become heroes for industrial operations. And this is exactly the kind of solution that Oxbow Intellect is providing—helping industries manage their stockyards with accurate, safe, and efficient drone-based volumetric analysis.
Why Stockpile Measurement Matters
Think of a stockyard as the pantry of an industry. If a cement plant doesn’t know how much limestone is available, production planning becomes a guessing game. If a power plant underestimates its coal reserves, it risks unplanned shutdowns. And if reports don’t match reality, it creates endless disputes between operations, finance, and procurement teams.
Accurate volumetric analysis ensures:
Clear visibility of inventory at any given time
Better procurement planning without last-minute rushes
Reduced material loss and pilferage
Audit-friendly reports that build trust across teams
In short, it’s not just about piles of raw material—it’s about making confident business decisions.
How Drones Changed the Game
Here’s the beauty of drones: they make a complicated, time-consuming job incredibly simple.
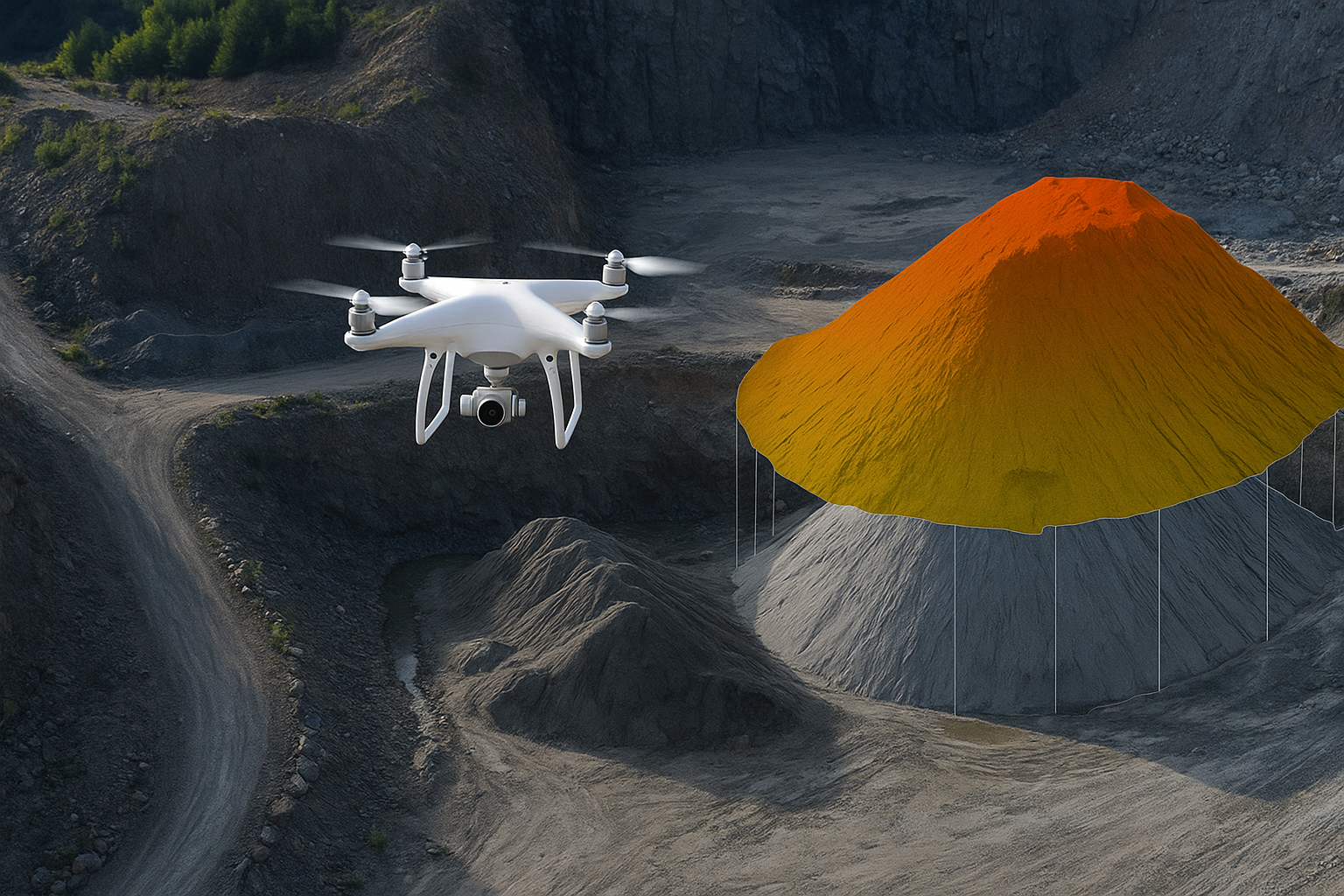
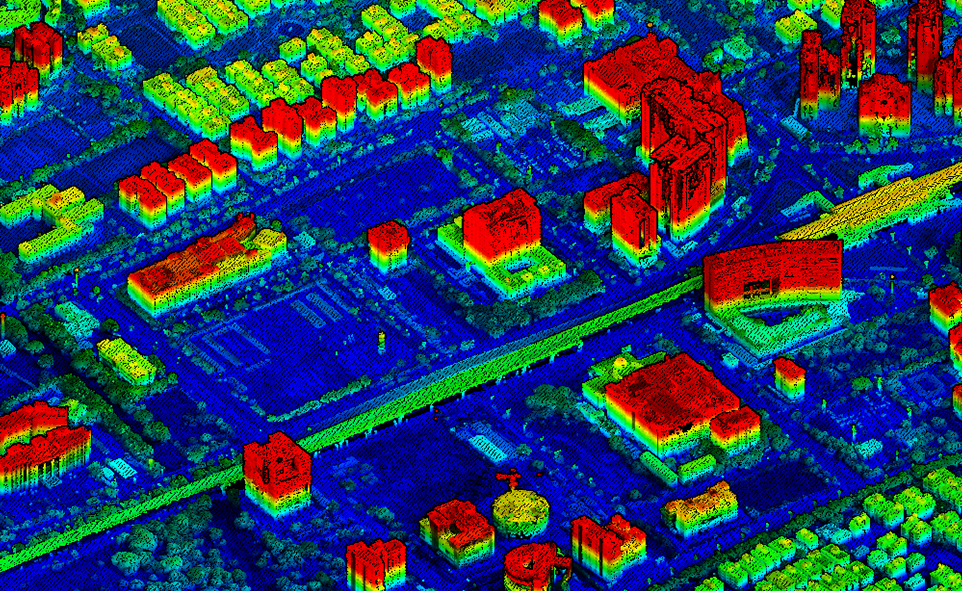
A drone flies over the stockyard, capturing hundreds of high-resolution images from multiple angles. These images are processed through photogrammetry software to create a detailed 3D model of the stockpiles. From there, precise volumetric data is calculated.
What used to take a ground survey team days can now be done in just a few hours—with accuracy that’s often within a few centimeters. No climbing unstable piles. No shutting down sections of the yard. No guesswork.
With Oxbow Intellect’s drone-based solution, industries don’t just get raw numbers—they get visual 3D models, trend comparisons over time, and reports that integrate smoothly into planning and audit systems.
Real Benefits for Industries
Time Savings
Traditional surveys can eat up days. A drone survey? Done in a morning, with reports ready the same day.
Accuracy You Can Trust
Consistent, audit-ready data reduces disputes between departments and with external auditors.
Safety First
Workers no longer have to walk across unstable piles or operate heavy equipment for measurement. Drones keep people out of harm’s way.
Cost Optimization
When procurement is based on accurate stock data, companies avoid both overstocking and unexpected shortages.
Visual Insights
3D models and orthomosaic maps generated by Oxbow Intellect give managers the power to see changes over time—spotting shrinkage, improper stacking, or even theft.
Stories from the Field
One mining company that switched to drone-based surveys said the biggest change wasn’t just in numbers, but in trust. Before drones, their finance team often questioned the stock reports provided by operations. After drones, everyone started speaking the same language—because the visuals and data didn’t lie.
At a cement plant, drone surveys helped reduce disputes with contractors over material handling. Both sides could look at the drone-generated report and agree on exactly how much material had been moved. No more finger-pointing, no more heated arguments—just clarity.
For Oxbow Intellect, these stories reflect the real goal of technology adoption: not just fancy tools, but better collaboration, safety, and smarter decision-making.
The Future: Smarter, Seamless Stockyard Management
What’s exciting is that drone-based volumetric analysis is just the beginning. With AI-powered analytics and integration into ERP systems, Oxbow Intellect is working toward giving companies real-time dashboards of stockyard inventory.
The vision? Automated drone flights that run on schedules, updating stockyard volumes daily or weekly without human intervention. Managers would simply log in and see updated figures and 3D visuals—ready with zero effort.
Imagine starting the day with your morning tea while checking a live dashboard that shows exactly how much coal, ore, or limestone is in the yard. That future is closer than ever.
Final Thoughts
Industries run on raw material, and raw material lives in stockyards. When stockyards are mismanaged, everything downstream—from production to profits—gets affected. Drone-based volumetric analysis is helping industries move away from guesswork and toward precision.
At the end of the day, it’s not about flying machines or fancy 3D models—it’s about people. It’s about giving managers peace of mind, keeping workers safe, reducing conflicts between departments, and ensuring plants keep running smoothly. With Oxbow Intellect providing drone-based volumetric analysis solutions, industries now have a trusted partner to make stockyard management safer, smarter, and more reliable. Drones aren’t replacing humans—they’re empowering them. And in industries where every ton counts, that empowerment makes all the difference.